2020 has been a perilous challenge for everyone across the globe. It was the year of the virus, from both a biological and a digital and cybersecurity perspective
We were unexpectedly infected by Covid19, a deadly and disruptive virus that changed our way of living. Thankfully, great strides are being made in therapeutics, and vaccines are on the way. The unexpected happened in 2020, and it served as an urgent wake-up call on the need for better pandemic preparedness.
Similarly, the digital scourge of cyber-attacks and breaches, exacerbated by the need for an ecosystem of immediate remote work to avoid Covid19, was calamitous.
Hackers took advantage of the gaps in new remote work environments as the global cyber-attack surface greatly expanded. Governments, companies, organizations, and individuals have paid a heavy price from breaches and from ransomware attacks—clearly, we were not adequately prepared for the digital virus either. 2021 needs to be the year for cybersecurity preparedness.
With most businesses operating remotely, in 2020 hackers stepped up attacks against an expanded and target-rich environment. Breaches almost doubled from 2019. The surge correlates to an expanded attack surface. This comes as no surprise because there were close to 4.6 billion Internet users active as of July 2020, representing 59% of the world’s population.
Internet users in the world 2020 | Statista Online crimes reported to the FBI’s Internet Crime Complaint Center (IC3) nearly quadrupled as a result of the COVID-19 pandemic.
In 2021, the work from home trend will continue and cybersecurity will continue to be a major challenge. According to Cybersecurity Ventures, it is estimated that cybercrime will cost the world $6 trillion annually by 2021. Cybersecurity Ventures envisions that a business will fall victim to a ransomware attack every 11 seconds by 2021.
The means and capabilities of attack for hackers are varied across levels of sophistication and depending upon the actors, some who are related to organized crime groups or, especially, nation states. Financial gains are still the main motivation behind most cyber-attacks. Phishing has been a tried-and-true method of gaining access to company and personal data.
It is usually done by employing a fake website which is designed to look like the actual website. The purpose of this attack is to trick the user into entering their username and password into the fake login form, which allows the hacker to steal the identity of the victim. Hackers can easily mimic known brand websites, banks, and even people you may know.
Another method of hackers to reap havoc has been the growing trend of ransomware. Although ransomware has been around for years, it has become a more prevalent method for hackers as they can operate under the cover of cryptocurrencies that are more difficult to trace.
Ransomware can hold computers, and even entire networks, hostage for electronic cash payments. Cybersecurity Ventures forecasts that global ransomware damage costs to reach $20 billion by 2021 — which is 57X more than it was in 2015. Cybercrime To Cost The World $10.5 Trillion Annually By 2025 (cybersecurityventures.com)
There a many more types of cyber- threats, and their impact is accelerated by machine learning and artificial intelligence technologies that are allowing hackers to pinpoint vulnerabilities in networks and on devices for exploits.
The fundamental question for most companies and individuals is what can be done to better protect data in the increasingly connected global digital landscape. Below are a few basic actions we can undertake to make ourselves safer.
10 Steps for Cybersecurity Protection in 2021
1) Learn: It all starts by having a risk management perspective. Learn what you need to do from open sources. Gather insights from informational resources available in the media. Network with those who have expertise or experience that mirrors your customized cybersecurity needs.
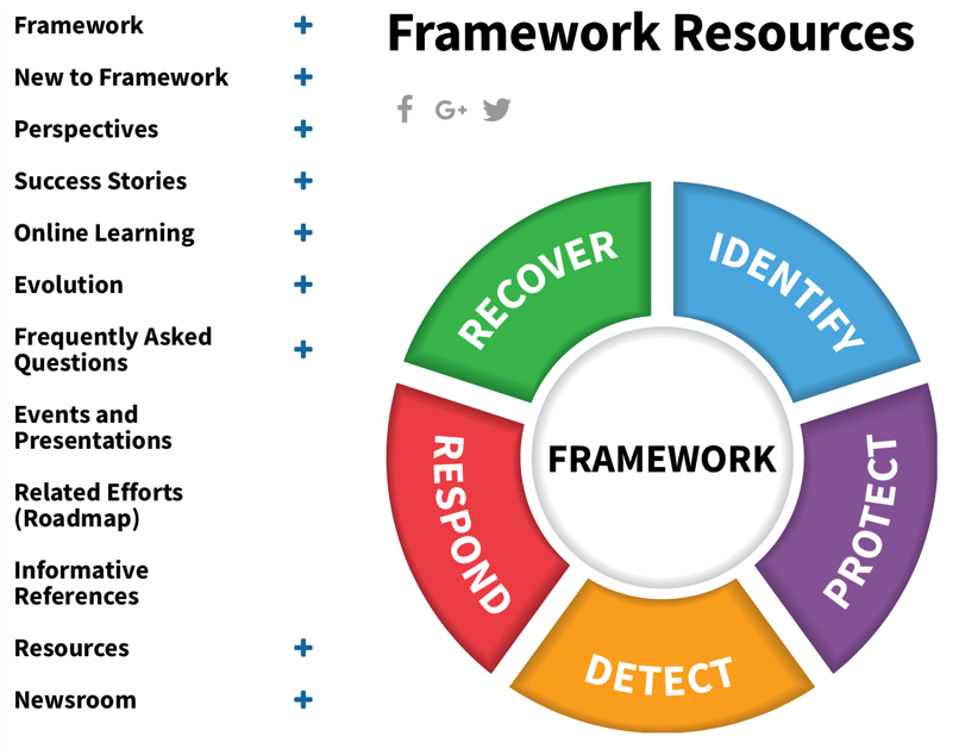
2) Create a Cybersecurity Framework: Explore Cybersecurity Frameworks such as NIST or MITRE ATT&CK®. which offer guidance on technical organization and response programs that identify and suggest means to mitigate gaps for cyber-threats. Cybersecurity frameworks are based upon lessons learned and continually modified to address new threats, including an incident response to a breach. Your goal should be to use these frameworks to create barriers to breach and policies for resilience.
3) Enact basic Cyber Hygiene: For example, do you have strong passwords and multi-factor authentication? Is your key data backed up? Do you use a secure WIFI? Do you need to use a virtual private network or encryption?Be sure to update your anti-virus software applications and regularly patch security flaws as they are updated. Referring
back to item #1, there are many good lists available on proper cyber hygiene you can adapt as your own. I recommend This CyberAvengers Graphic:

4) Be on the lookout for social engineering attacks: With the volumes of social media information out there on your personal likes and dislikes, hackers can figure ways to reach out to you with malware via phishing. Always look at who the emails or texts are actually from (not who they pretend to be from), and do not open up any files that are suspicious. Always be suspicious and operate on the premise of zero trust when it comes to social engineering threats.
5) The Internet of Things (IoT) has arrived and prepare for it: Each IoT device represents an attack surface that can be an avenue into your data for hackers. A Comcast report found that the average households is hit with 104 threats every month. The most vulnerable devices include laptops, computers, smartphones and tablets, networked cameras and storage devices, and streaming video devices, a new report found. Cybersecurity report: Average household hit with 104 threats each month – TechRepublic An important step to take is tochange your default passwords on any IoT devices you have in your network.
6) Consider outsource security services: If you have a small or medium sized business, consider bringing in outside cybersecurity expertise or managed service. They can augment your security posture with your internal IT shop and perform vulnerability assessments and recommend solutions and services that are most applicable to your industry requirements.
These are six basic actions to make cyber life easier in 2021. Nobody is fully invulnerable to breaches, but we can all take actions to improve cybersecurity. Wishing you a cyber-safer, healthier, and happier 2021!
Source: Forbes
2021 Cybersecurity Predictions: The Intergalactic Battle Begins
US Agencies and FireEye Were Hacked Using SolarWinds Software Backdoor